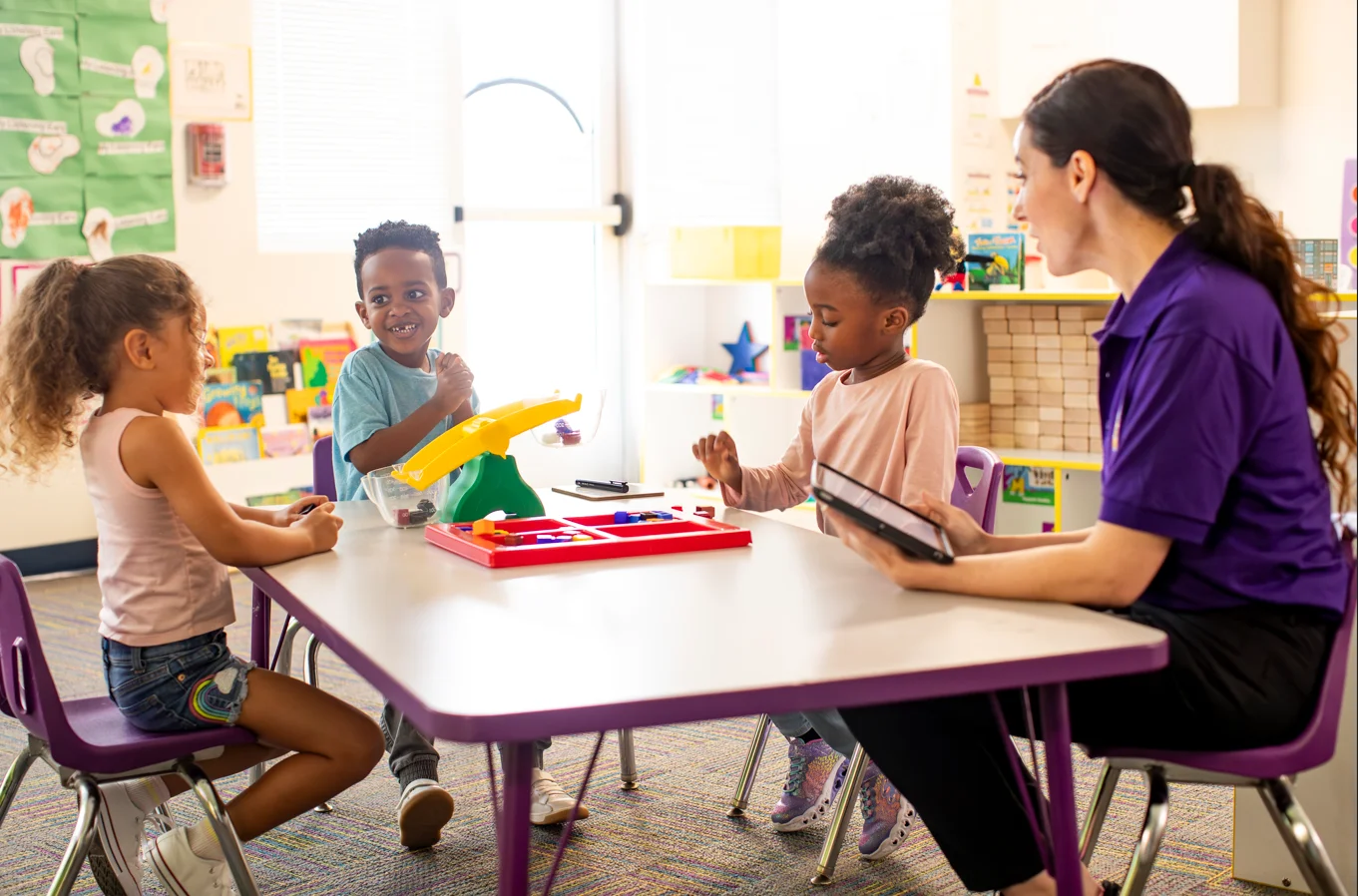
Early childhood education is key because it establishes a foundation for a lifetime of learning. This is where kindergartens come into the picture, an important part of nurturing this initial development. They provide a controlled, supportive atmosphere and assist young students in building cognitive, social, and emotional capabilities. Exploring how these learning environments influence early learning can benefit educators, parents, and communities.
Establishing a Safe and Engaging Space
A great kindergarten environment encourages exploration and discovery. In most classrooms, bright, stimulating materials, such as puzzles, art supplies, and educational toys, capture students’ curious minds and fill the rooms with engagement and inspiration.
These tools enable hands-on learning, providing children with the flexibility to experiment and learn at their own pace. Teachers also essentially create a safe space where young minds feel comfortable expressing their thoughts and ideas and taking intellectual risks. This nurturing environment helps set the stage for confidence and enthusiasm in learning.
Interaction to Develop Social Skills
Socialising is an important aspect of early learning. A Docksland kindergarten can provide children with an opportunity to interact with other children for group-related tasks. Through these interactions, they learn valuable skills such as sharing, cooperation, and empathy.
Group storytelling or other collaborative games help children master the art of communication. In addition, the teacher guides these interactions, modelling appropriate behaviours and conflict-resolution strategies. Such guidance helps children develop the social skills necessary for academic and personal success later in life.
Encouraging Emotional Growth
Emotional development is just as important as cognitive and social development. In a kindergarten, children are encouraged to develop emotional intelligence, which means that they learn to identify feelings and manage them. Through storytelling and role-play, teachers discuss how we feel things inside the body and express different emotions.
These exercises help young learners feel their own emotions, think about how they might promote the emotions they are expressing, and consider how other people might respond to the method behind such games. Kindergartens grow emotional literacy and provide children with tools to grapple with complex social situations.
Supporting Cognitive Development
Cognitive development in the early years focuses on language, problem-solving, and critical thinking skills. Play-based learning strategies are widely used by kindergartens to promote cognitive development.
Puzzles, music, and storytelling promote language development and cognitive skills in children. Through interaction, teachers provide instruments to introduce concepts that stir early, curious minds with inquiry. This allows children to learn in a fun and engaging way and cultivates a lifelong interest in learning.
Inculcating a Love for Learning
Instilling a love for learning from a young age will go a long way in your child’s education. The goal of kindergartens is to create this zeal for learning by designing interesting and interactive learning experiences.
Through creative and exploratory activities, children learn to associate education with enjoyment. This creates a positive association that encourages them to develop a thirst for knowledge as they journey along their educational paths. The teacher is responsible for creating lesson plans that interest students and fire their imaginations.
Laying the Groundwork for Future Learning
Kindergarten is not just about early education; it is about cultivating skills and attitudes students will use for the rest of their lives. These crucial years build the foundation for educational success and maturation.
Children with quality early education are more likely to be great critical thinkers and adept at adjusting and adapting. Kindergarten education pays off with better grades, better social integration, and stronger emotional foundations for the years to follow. Children need to have a good bedrock of these elements in order for them to flourish across varying settings.
Involving Families in the Learning Process
When a family is involved in early education, a child will be more motivated to learn. Many kindergartens promote parental participation through consistent communication and involvement in classroom activities. This collaboration helps to create a learning community where parents and educators reinforce the child’s development.
Families who are involved share great information about a child that highlights their strengths and where they may need help. Such collaboration helps ensure that children continue to be supported both at home and at school.
Conclusion
Kindergartens are at the heart of early childcare education, with a holistic solution for holistic learning. As early childhood education focuses on overall cognitive, social, and emotional development, it provides a well-rounded base for future success.
Giving priority to exploration, interaction, and emotional consciousness helps parents prepare their children to deal with the complexities of the world. Kindergartens, too, are changing, but they continue to have a critical place in supporting early learning. When educators partner with families, these institutions can improve the early learning experiences of children, establishing a trajectory for lifelong learning.